The Suffolk Masonic District and Suffolk Post 23 MWV dedicate a bench for the Battle Within Foundation at the West Sayville Golf Course and Lt. Michale Murphy Navy Seal Museum.
The bench was placed and dedicated by the Suffolk District teams, led by R:.W:. Robert Licata, DDGM of the Suffolk Masonic District and members of Suffolk Post 23, MWV.
The LT Michael P. Murphy Navy SEAL Museum tells the story, sacrifices, and legacies of the Special Operators of Naval Special Warfare Command from the frogman and Underwater Demolition teams of WWII and Korea to the birth of the SEALs in Vietnam, the War on Terror, Operation Redwings, and an exhibition hall dedicated solely to the SEAL Training program.
The Battle Within Foundation:
In the past 40+ years, since the end of the Vietnam War, we have lost more American heroes due to suicide than all foreign wars and conflicts in that time period combined. Despite the very best efforts of family, friends, the VA, and scores of highly dedicated veteran-based organizations, approximately 20 veterans each day are lost to us due to complications from wounds and injuries we cannot see.
That’s 7200 brave men and women a year who volunteered, stood on the yellow footprints and swore an oath to God to protect and defend our country. They proved this commitment, many seeing and experiencing the unimaginable in our name. Unfortunately, they made it through one war, only to come home to fight another.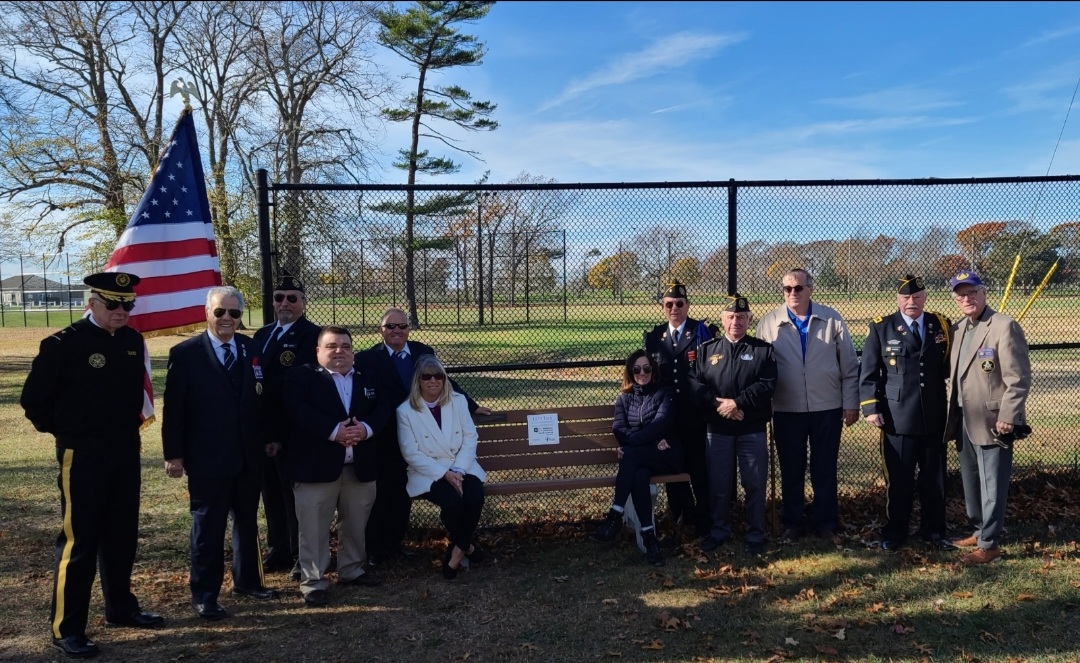 
The Battle Within Foundation has been at the forefront of Veteran PTSD research and assistance to troubled veterans.
Supporting veterans in crisis, educating the public, and honoring our heroes for their service, regardless of where they died.