Brothers,
Over the last few weeks, several messages have come down to the brothers about possible scams, and most recently, a cowan, eavesdropper, or worse, who has been trying to sit in meetings in other states. It’s important to keep our brothers safe from scams and our Lodges free from cowans and eavesdroppers.
Let’s start with scams. We are all pretty much aware of the infamous “Nigerian Prince, government or other” scam. However, these scammers have grown and evolved over time, and their tactics have evolved as well. We, as Masons, are usually of the type that wants to help someone in need, especially a brother Mason. The scammers know this and will use it against their targets. They will craft well-written emails and send them to a hacked e-mail list in the hope that someone will reply that seems sympathetic or at least willing to engage in dialog. This is where the social engineering part comes in.
Some things to look for.
- If you receive an e-mail from a Brother, even a Brother that you know personally, that requests you help them with some issue, usually financially; Trust but verify is the best way to handle this. If you know the Brother, call him to find out what the issue is and if it is legitimate.
- If the requester has a reason he cannot speak on the phone, be wary. Some scammers are very convincing in messages (e-mails, Instant messages, or text), but cannot talk on the phone because you will know the jig is up.
- If the person contacting you insists you send money, typically in an odd way, like gift cards to some other untraceable way. This is a huge red flag.
The way to spot a scam e-mail or text:
- Typically, a scam e-mail or text at a glance will look normal, look closer and you will see some serious grammatical or spelling issues. Scammers do this on purpose. Most would immediately discard the message knowing that the sender is a scammer but if the receiver is willing to overlook these minor errors, they may have a better chance of convincing someone they are who they are not.
- Look at the actual e-mail address or sender address. It is easy to “spoof” some emails with a name displayed instead of the actual e-mail address. Once you can see the sender, the scam is exposed.
- Look for any cc or bcc in the e-mail. If you see the e-mail or message is to you but also to “Undisclosed Recipients”, again a huge red flag.
There are several good websites that will explain how to spot a scam message if you are unsure have someone you trust have a look at it before you hit reply. Remember scammers will always put emphasis or urgency to the message to stop you from checking on the legitimacy of the scam.
Now on the trickier subject of Cowans and Eavesdroppers:
Back in the day, Lodges has to deal with Cowans more often than you think. This was due to the support network that Masons are famous for. if you were a Brother and taking a long or difficult trip and found yourself stranded you could always contact the local Lodge and they would always help out with a place to stay, a meal maybe event help you out of a cash problem and send you on your way. This is where our dues cards came from. Its wasn’t enough just to say you were a member you needed to prove it through lawful Masonic information. The Cowans had maybe read enough exposes to know some or just enough to get over, but no dues card was a no go.
Over the years and with more and more government social services in place it was not really necessary to “get over” on the Masons for a freebie anymore so dealing with Cowans died down. This was much bigger problem in the 1st half of the 20th century in the US.
Jumping to the 21st century, the problem has slightly risen again, this time not for free “hots and a cot” but for another purpose. This time it seems most of the ones in recent years were about pretenders just wanting to get into a Lodge meeting, like those who explore forbidden buildings. The pretender’s motives may be unclear, but dangerous just the same.
These seems to be a growing group of individuals who think since they have read the books on Freemasonry or even joined a clandestine Lodge or got suckered into membership in the thousands of scam Illuminati sites, that they are members worldwide who can visit any Lodge in the world. The most recent warning comes from the Grand Lodge of Alabama who had a member who renounced his membership yet later turns up in other states and attempts to sit in a Lodge.
We have many statements in our obligations and in Masonic law that every brother should know. Any strange man that comes to your Lodge should be examined. This could mean several things. The first and foremost is to ask for his dues card. We all received permanent dues cards a few years back. These cards have a QR code on them.  A quick scan of the QR code on the card using the Amity phone app also available on Google play, will get you his current status as a Mason. Of course, this is only for US Masons and not every jurisdiction uses them, but most do, many are on the same MORI system that the GLoNY is. Travel outside the US is a discussion for another time.
A quick scan of the QR code on the card using the Amity phone app also available on Google play, will get you his current status as a Mason. Of course, this is only for US Masons and not every jurisdiction uses them, but most do, many are on the same MORI system that the GLoNY is. Travel outside the US is a discussion for another time.
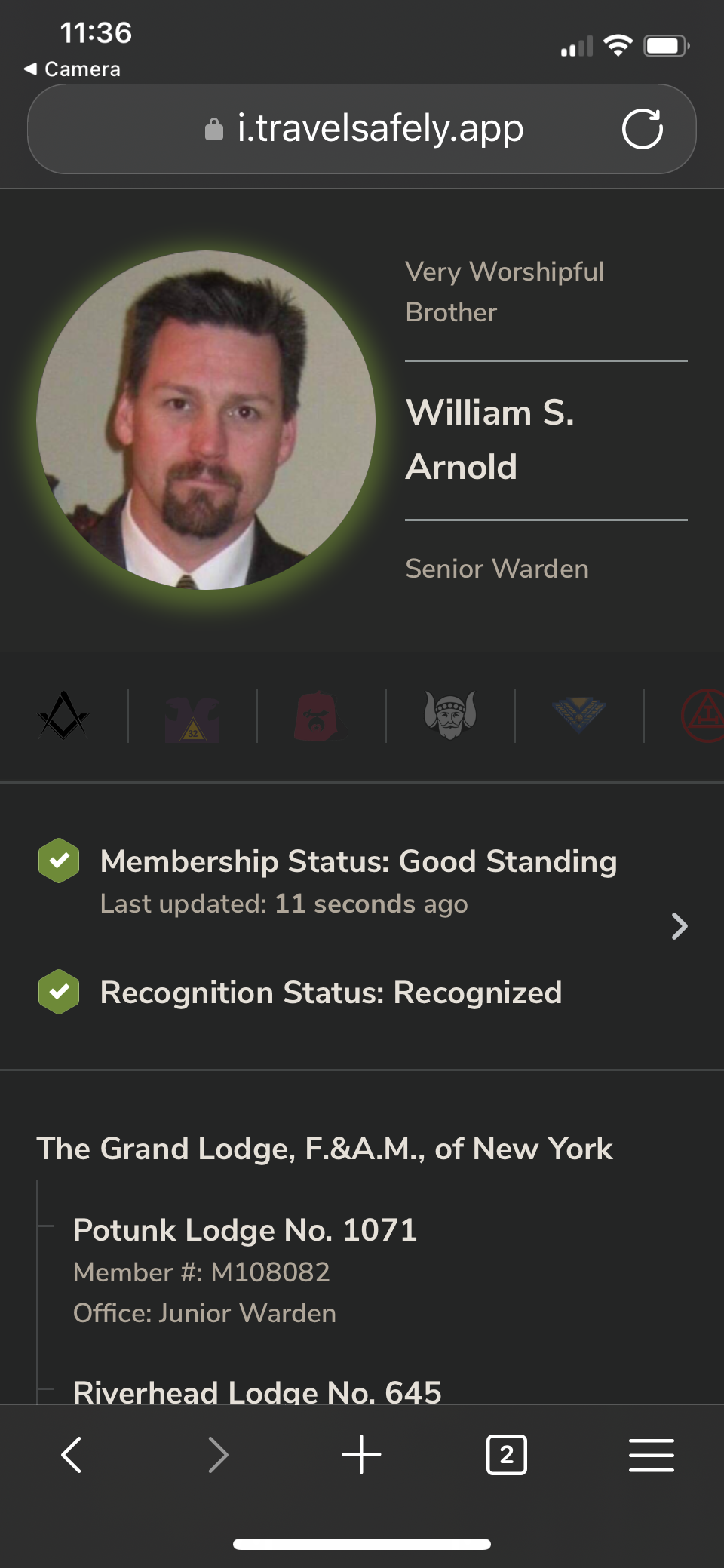 We all encourage our Brothers to travel and it’s one of the best benefits of being a Brother. However just showing up at a Lodge where nobody knows who you are, well you should not be offended if you are challenged before you are allowed to join the meeting.
We all encourage our Brothers to travel and it’s one of the best benefits of being a Brother. However just showing up at a Lodge where nobody knows who you are, well you should not be offended if you are challenged before you are allowed to join the meeting.
This is the Brothers doing their due diligence. There have been a few changes to Masonic Law in recent years with regards to opening/closing on any degree. This some have issue with and some welcomed. But has led to a bit of confusion. Once a gentleman is initialed, given the EA degree, does this give this new Brother right to travel? Once they are put in the system by the secretary, they will receive a dues card in short order or at least their GL number. My opinion on this is no, they are still to be treated like EA’s & FC’s were prior to the changes. This means they should not travel to other lodges by themselves. They need to be vouched for and escorted just like before. All Masters of Lodges should instruct their Sr. Deacons at least as such, well that’s his job after all. I have asked this question before and have gotten different answers, so please check with your DDGM if you need clarification. So, when we open a lodge and the Sr. Deacon’s, Jr. Deacon’s & Tyler’s responsibilities are given, do we pay attention?







 A quick scan of the QR code on the card using the
A quick scan of the QR code on the card using the  We all encourage our Brothers to travel and it’s one of the best benefits of being a Brother. However just showing up at a Lodge where nobody knows who you are, well you should not be offended if you are challenged before you are allowed to join the meeting.
We all encourage our Brothers to travel and it’s one of the best benefits of being a Brother. However just showing up at a Lodge where nobody knows who you are, well you should not be offended if you are challenged before you are allowed to join the meeting.